Bollore Logistics (18 May 2021) - Problem Statement (1)

Automated human tasks, and automated product handling with small changeover time.
For startups with Technology Readiness Levels of 4 & above.

Infineon (31 Aug 2021) - Problem Statement (2)
Objectives:
- Establish integration tools for data extraction, transformation and loading.
- Develop AI data processing platforms.
- Scalable for operations implementation.
- Enable domain experts to perform data analytics independently.
Desired Outcomes:
- Focus on predictive maintenance for automated material handling equipment.
- To package prototypes into a suite of recommended platforms and tools.
- Develop AI algorithms related to the project scope.
- AI SMART Discovery: Demonstrate capability for prototype analytics for the layman.
Current Limitations:
- Problem centric data analysis: Engineers must analyse a voluminous amount of data for actionable insights through various data sources (OEE, yield, product data & recipes, machine alarms, etc.).
- High effort, time and subject matter knowledge are required for effective cause and effect analysis.

Bollore Logistics (18 May 2021) - Problem Statement (2)

Alternative transport modes, fuels, packing materials & end-to-end services.
For startups with Technology Readiness Levels of 4 & above.

Bollore Logistics (18 May 2021) - Problem Statement (3)
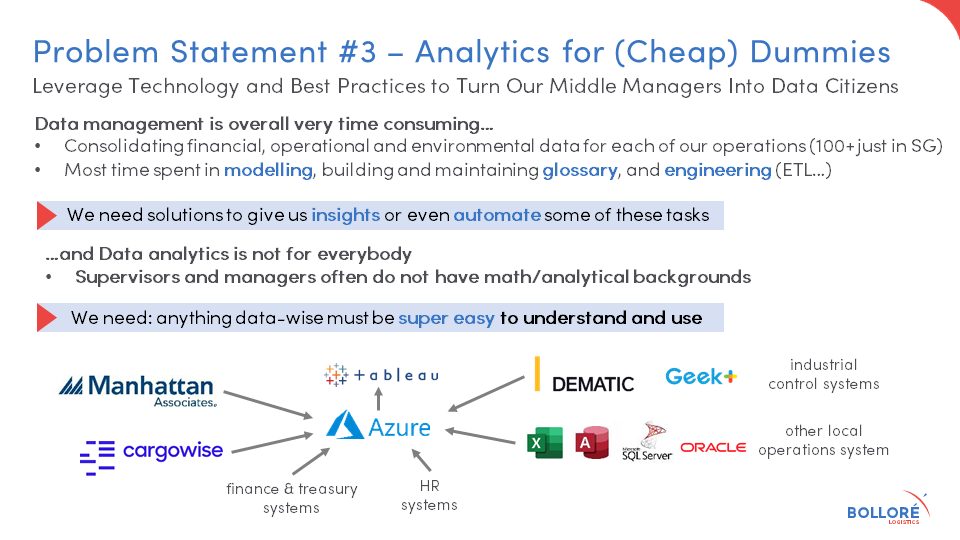
Technology and best practices to turn our middle managers into data citizens.
For startups with Technology Readiness Levels of 4 & above.

Bollore Logistics (18 May 2021) - Problem Statement (4)

Perfect low-code platforms to capture more relevant data and improve efficiency.
For startups with Technology Readiness Levels of 4 & above.

Infineon (31 Aug 2021) - Problem Statement (1)
Objectives:
- Automate tasks assignment and prioritisation based on technical requirements and technicians’ profiles.
- Optimise execution with a grouping of tasks to improve efficiency.
- Predict the demand vs supply and forecast the overtime planning.
- Identify the technical competency gap among technicians.
Desired Outcomes:
- Over 34 technicians with different skillsets for operation and engineering tasks are complex and vary widely, from logistical units collection to equipment setup.
- To have a one-stop solution platform between managers, engineers and technicians.
- Interactive solution on a mobile device for technicians to receive notifications and report efficiently.
- If the execution of tasks can be on auto-pilot mode and optimised continuously driven by data analytics, this would significantly improve work efficiency.
Current Limitations:
- Engineers need to manually book the necessary resources, including equipment and technicians’ availability.
- Independent systems are used to check and book different resources, e.g. equipment booking, technician scheduling, engineering samples, etc.
- Manual and tedious effort on engineers to communicate, cross-check, and set priorities with managers and teammates.

Schneider Electric (18 May 2021) - Problem Statement (1)
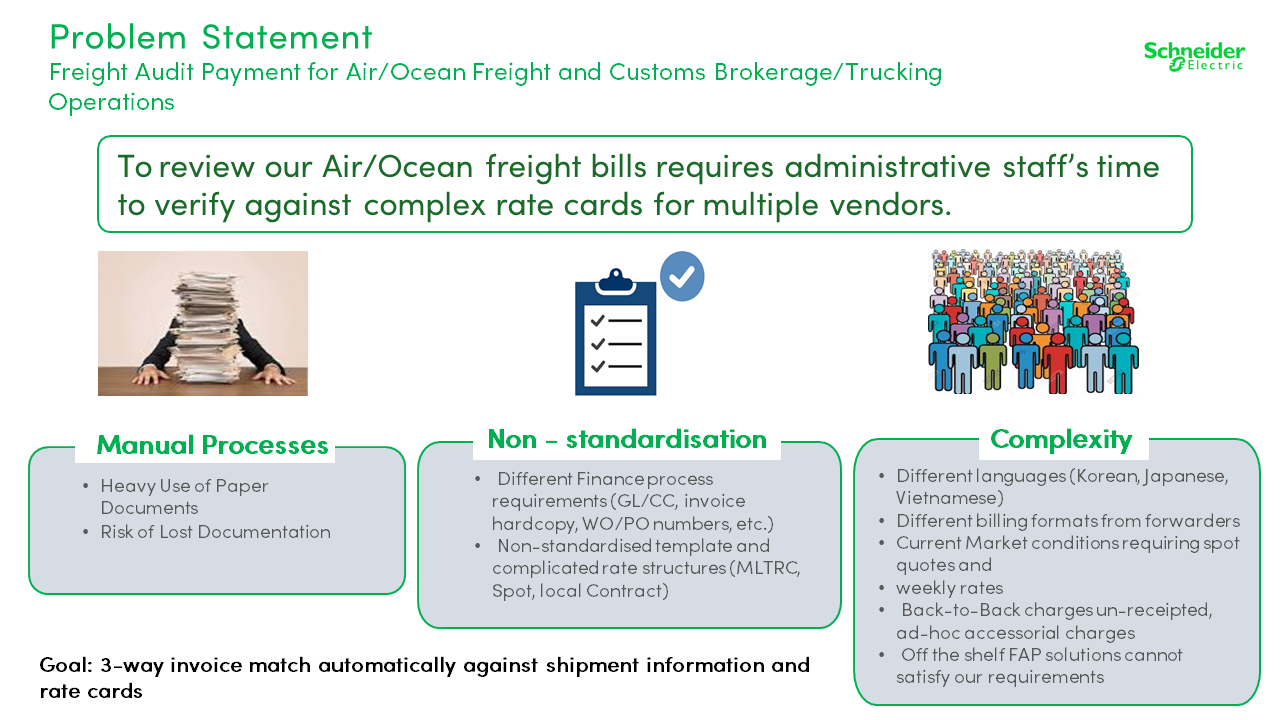
Automatic 3-way invoice match against shipment information & rate cards, for air/ocean freight & customs brokerage/trucking operations.
Open to providing relevant startups with data sets & more information.