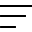About the Problem Statement:
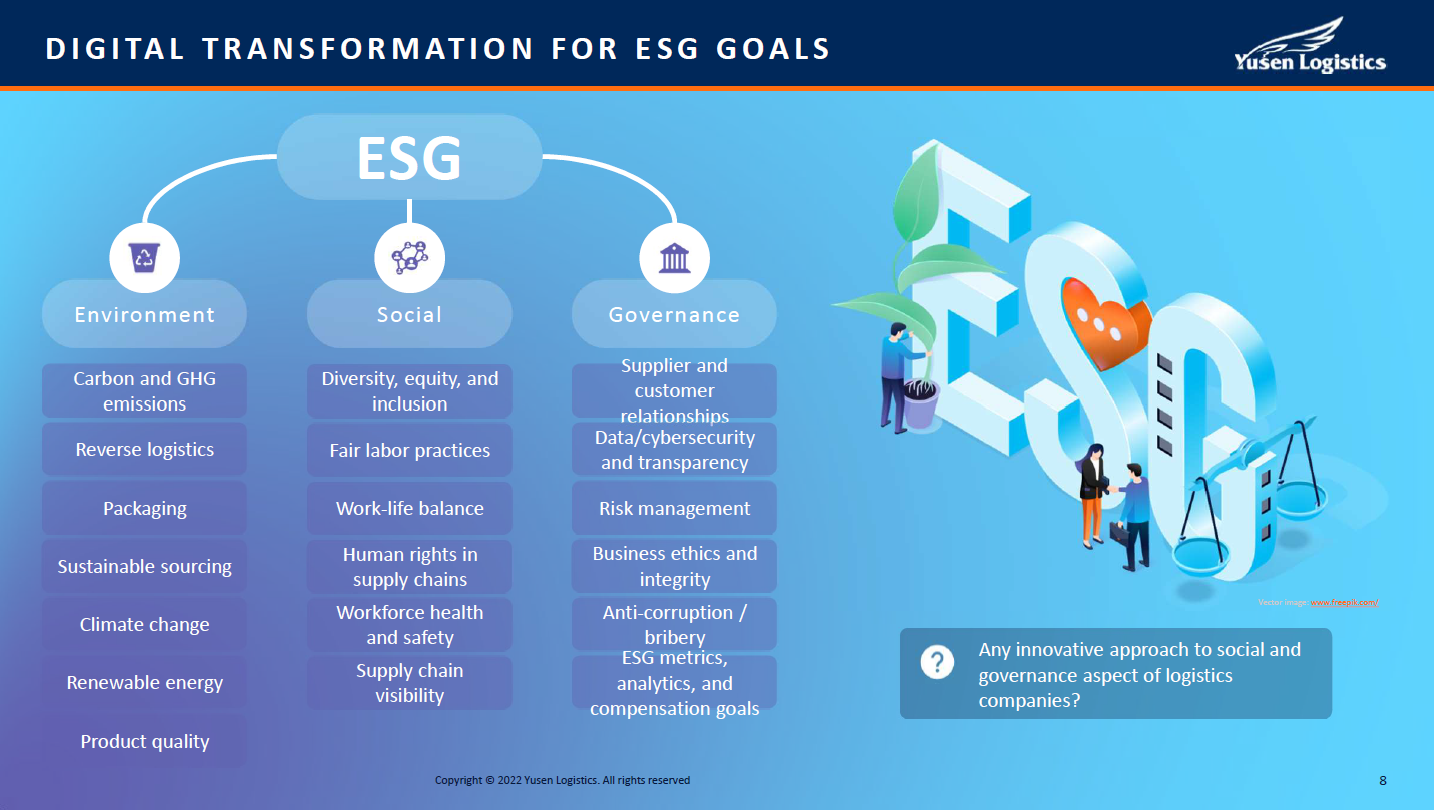
Freight transport is a large contributor to emissions of CO2 and customers look for supply chain partners who prioritise Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) goals. Customers often ask us to optimise logistics concerning cost and efficiency in their supply chains. Recently, we have been asked not only to optimise logistics but also to propose ways to reduce the environmental impact of logistics. In other words, they are looking for the best balance between logistics optimisation and environmental impact. To meet this new demand, it is necessary to visualise the CO2 emissions from air, ocean, and land transportation with transportation data.
For air and ocean freight forwarding, the estimated amount of CO2 emissions can be calculated through current shipment data from the organisation’s operations system.
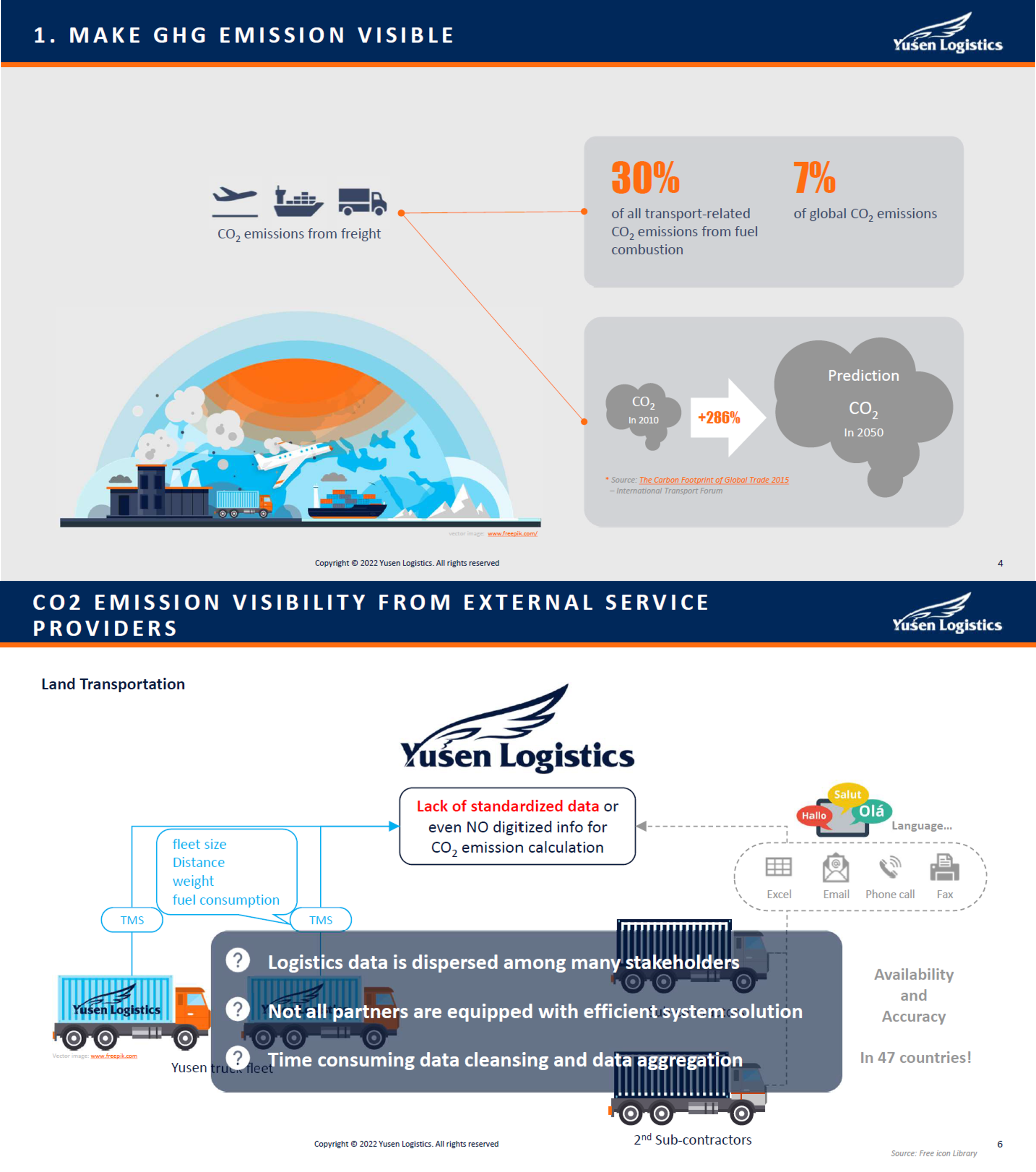
Yusen Logistics owns its trucks for land transportation and works with many partner companies in many countries. The number of subcontractors is so large that it takes a considerable amount of time to collect the necessary data from all the subcontractors and a great deal of effort to organise the data. This is because each company has its transportation management methods and IT systems. Some of them even manage the data manually. In addition, the transportation data is handled in various foreign languages, which takes time to translate.